Server security is an essential responsibility of system administrators to protect the valuable data from evolving cyber threats. Businesses can reduce risks using the server security checklist and enhance their system’s resilience for a secure web server. We cover the top 20 best strategies for server security and industry-leading tips.
Key Takeaways
- Understand the crucial importance of server security.
- Discover 20 expert tips to strengthen your server’s defenses against cyber threats.
- Learn about common server security issues and how to mitigate them effectively.
- Explore best practices like regular backups, SSL certificates, strong password security, and more.
- Gain insights into server security policies and network segmentation.
- Find out how to secure remote desktop access and limit server access to essential users.
- Explore the benefits of two-factor authentication and intrusion detection systems.
- Understand file auditing, service auditing, and virtual environment isolation.
- Stay informed about the latest server security strategies to ensure your online safety.
Server Security Explained
Server security refers to the measures and practices taken to protect a server from unauthorised access, data breaches, and other security threats. It involves using various security protocols and prevents potential vulnerabilities that hackers or malicious actors can exploit.
The primary objective of server security is to protect the integrity of your server’s resources. It also protects the services and data stored on the server. Server security combines administrative and technical measures. These measures include:
- Using robust cybersecurity software.
- Creating complex passwords.
- Deactivating unnecessary services and ports.
- Managing user privileges.
- Monitoring and logging tools.
Server security stretches past technical measures. To truly secure your server, present-day organisations have security assessments. They use risk evaluations and security protocols that help remove potential vulnerabilities.
Why is Server Security Important?
The danger that businesses face from cyber attackers cannot be overstated. On top of direct monetary losses, a security infringement can damage the brand’s reputation. Companies like Yahoo have been implicated in significant data breach scandals, but smaller businesses are also at risk. A 2023 study indicates that small businesses are the target in approximately 43% of cyberattacks
Maintaining robust server security is vital to safeguard your business from hackers. Servers often store invaluable personal details, credit card data, and business secrets, making them attractive targets. To mitigate this risk, you need effective server security. Intrusions can lead to data theft or server malfunction. The same study shows more than 74% of breaches involved the human element. It includes social engineering attacks, errors, or misuse.
Cybercriminals often exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software. Regular updates help patch these weaknesses, making access harder. Server security is critical to maintain operations and safeguard data. It ensures regulatory compliance and preserves trust in your organisation.
What are the Common Server Security Issues?
Understanding server security is critical for individuals and businesses to ensure the safety of their digital assets. As technology evolves, so do the threats, requiring an ongoing commitment to address and manage security risks. Highlighted below are common issues around server security:
- Weak Passwords – Easy-to-crack passwords invite unwanted access.
- Outdated Software – Old software versions have known exploitable vulnerabilities.
- Imperfect Patch Management – Missing patches leave security gaps.
- Improper Network Port Configuration – Misconfigured ports can be easily exploited.
- Neglected or Old User Accounts – Unused accounts become easy targets.
- Inadequate Physical Security – Lacking hardware protection invites onsite breaches.
- Malware Attacks – Threatening programs damage or disrupt systems.
- Data Breaches – Unauthorised data access compromises privacy and trust.
- Insecure System Settings – Default or relaxed settings heighten risk.
- Non-compliance to Security Policies – Ignoring compliance guidelines weakens overall security.
- Insufficient Security Software – Lack of software allows potential breaches.
- Unprotected Virtual Servers – Virtual environments need specific security measures.
- Lack of Encryption – Unencrypted data can be stolen or altered.
- Unmonitored Server Activity – Untracked activities make threat detection difficult.
20 Server Security Best Practices and Tips
The 20 tips for server security hardening measures present a comprehensive guide to securing and optimising your server effectively.
Server Security Checklist
1. Upgrade Server Software and Operating System.

Regularly upgrading your software and operating system security is essential. With the software up to date, you can protect against known vulnerabilities and take advantage of the latest security patches.
It prevents hackers from exploiting weaknesses in your system. For instance, maintaining the latest version of your server’s operating system, be it Linux or Windows, is essential. Regular updates also ensure that you have access to new features that enhance the overall server security.
2. Regular Backups

For optimum server security, regular server backups are essential. The practice safeguards against potential loss following a security breach or system malfunction.
It’s crucial to incorporate encryption for data during the backup procedure. It provides an extra security layer of protection of sensitive data on the server.
The 3-2-1 backup rule is a best practice strategy to protect valuable data. It suggests having at least three copies of your data, two localised but on different mediums, and one offsite backup.
3. User Access Limitations
Access restrictions enhance security significantly. It involves limiting user permissions and granting access rights strictly to those required.
Robust authentication methods, for example, two-factor authentication, to boost security. Regular inspections and updates of access control measures are advisable to eliminate redundant privileges and accounts that are no longer required.
Every server has a root user with full command access, a prime target for hackers. To enhance security, disable the root login for SSH and create a limited user account for admin tasks. The method restricts root user access to only essential usage and limits threat exposure.
4. SSL Certificates

SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificates and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are essential to server security. They ensure encrypted communication between your server and the client, contributing to safer data transmission over the internet. It’s a defence against unwanted access and potential data breaches, making it integral in protecting your data.
5. Enhance Security with a VPN

A Virtual Private Network (VPN) offers additional security by encrypting data traffic between your device and the server. It creates a secure channel that inhibits potential hackers from intercepting sensitive information. Combining SSL certificates with VPNs improves your server security, ensuring a safer online environment for data retention.
6. Strong password security

Using complex passwords with a minimum length of 12 characters is recommended. It includes combining uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols. Regularly updating and changing passwords is also crucial to mitigate the risk of breaches. Consider using a password manager tool to securely store and generate strong passwords for all accounts on your server. Some password security tips include:
- Add rules for minimum password length and complexity.
- Steer clear of password storage using reversible encryption.
- Use a lockout mechanism for repeated failed attempts.
- Add a session timeout after a period of inactivity and enable dual-factor authentication.
7. Firewall Protection
An essential component of server defences is a firewall. It acts as a shield between the server and the outside online world. It monitors all incoming and outgoing network traffic, screening and blocking potential threats.
The firewall manages access according to public, private, or internal service types. It ensures security while maintaining necessary functions. A server control panel can set up and manage firewall rules. In CloudPanel, firewall management involves a few simple steps.
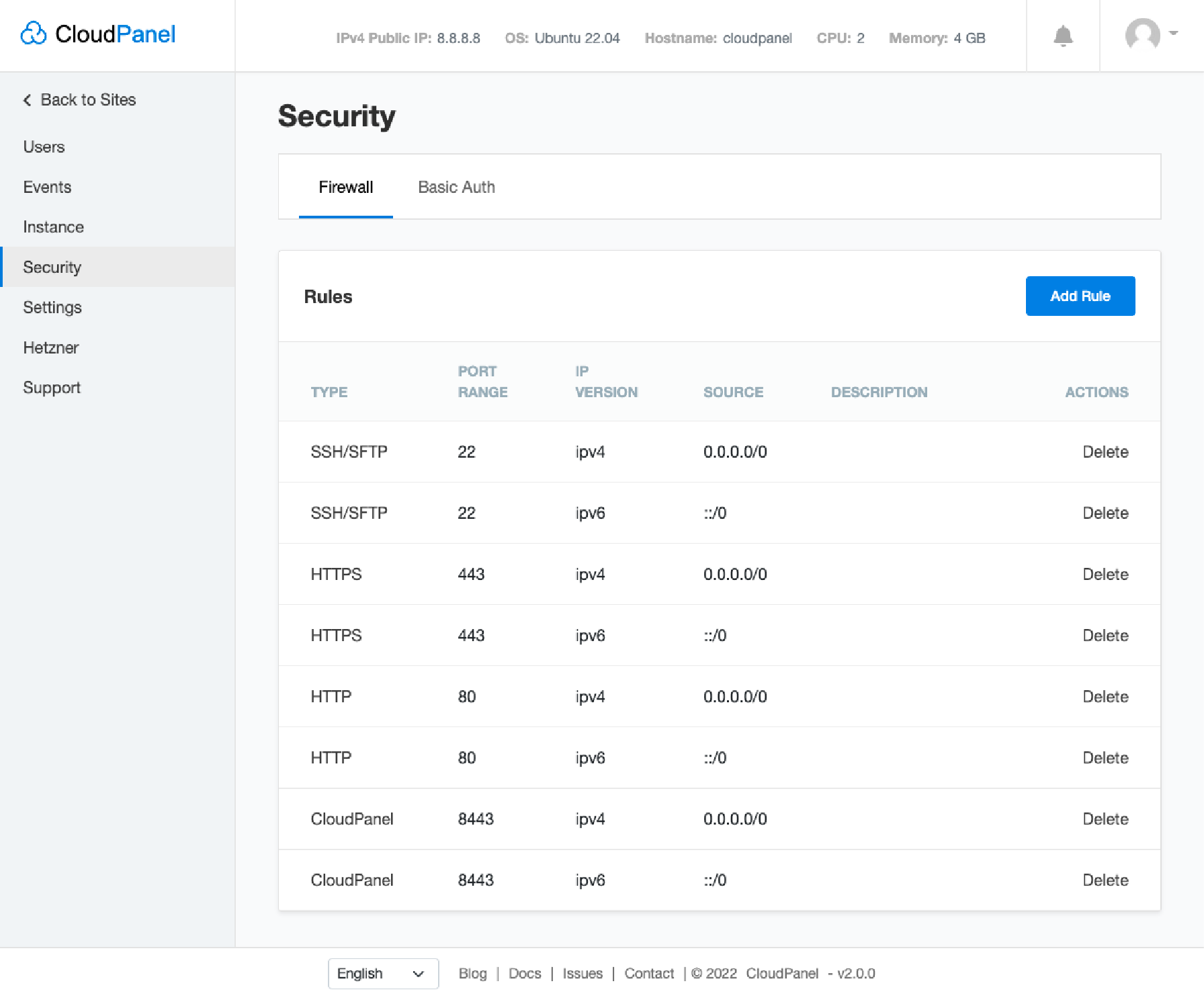
- Go to Security in the admin area.
- Click Firewall to see a list of pre-configured firewall rules.
- You can edit or create new rules by clicking the Add Rule button.
- Specify the TCP/UDP port range and IP addresses.
- You can also add or delete rules according to your needs.
Remember, regularly reviewing and updating these rules contributes to maintaining a secure server environment.
8. Security Patch Management
Patch management regularly updates server software with service providers’ most recent security patches. It also involves scheduling their installation during off-peak times. It is essential to document this process, automate where possible, and ensure IT staff know its significance.
9. Secure Server Connectivity
SSH Secure Shell and VPN (Virtual Private Network) measures can establish a secure connection between your device and the server. It ensures that sensitive information is encrypted and transmitted safely.
A strategy to authenticate an SSH server is to employ a random port number from 1024 to 32,767. It makes hacking attempts less likely by intruders.
10. Server Logs and Security Tools
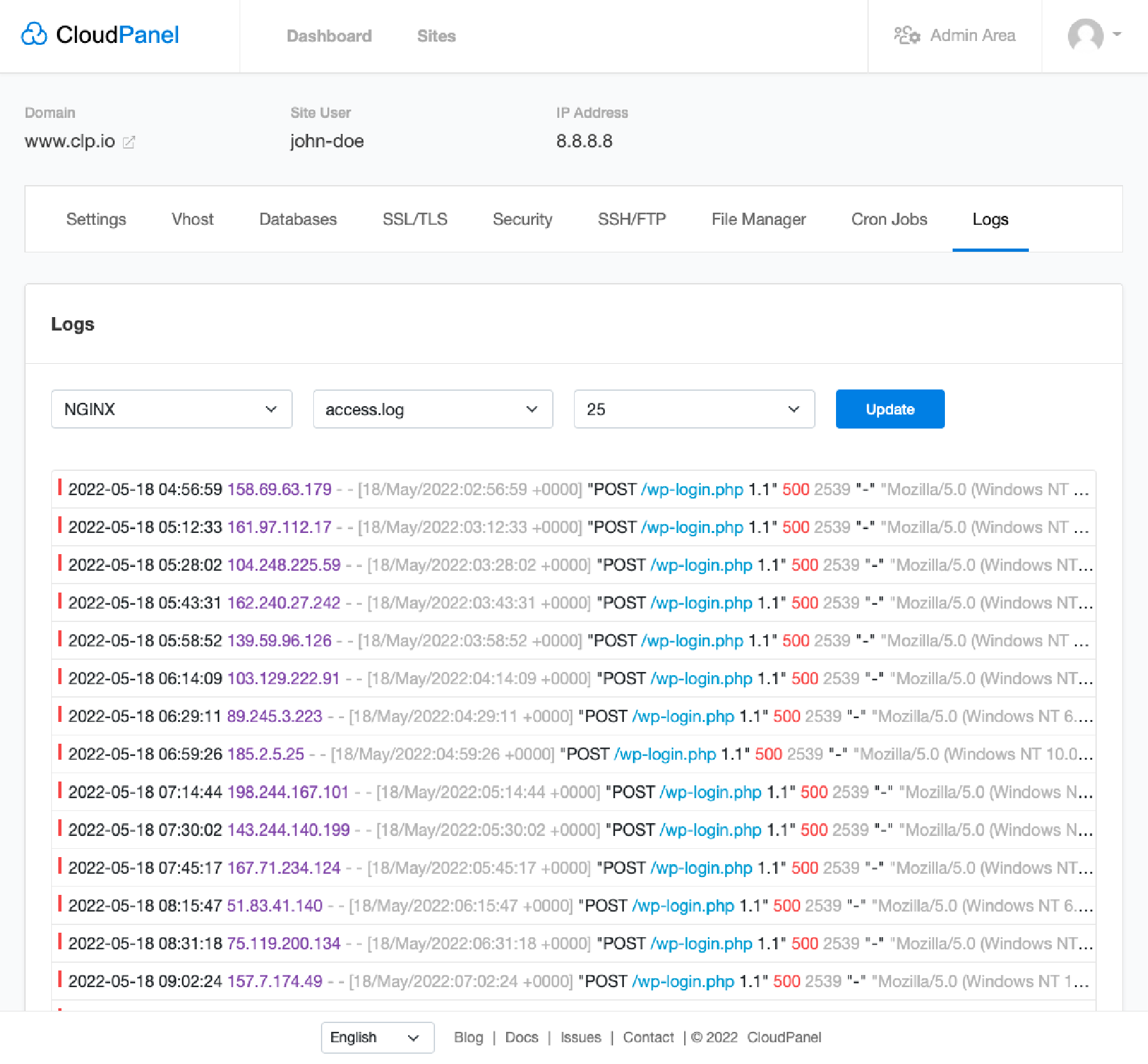
Server logs provide a record of activities on the server. It allows system admins to track and monitor suspicious access attempts. Regularly reviewing the server logs allows potential threats to be detected early, and appropriate actions can be taken to mitigate them.
CloudPanel offers extensive server logs which monitor all system activities. Users can access NGINX and PHP-FPM log files to ensure proper function and review potential server issues.
11. Security Policies
A security policy outlines the rules and guidelines for your IT organisation to ensure optimal server security. It should include strong password requirements, user access controls, and network restrictions.
In addition to policy standards, it should include employee training about recognising potential threats and following safety practices. You can add a regular review process to update it according to new potential threats or regulatory changes.
12. Network Segmentation
To secure a server, network segmentation is a valuable security practice. The process involves dividing your network into smaller parts to reduce exposure to security risks.
It limits the impact of a potential breach to one segment, protecting valuable data on other segments. Securing your server is considered a strong security hardening measure, aligning with web server security best practices.
13. Securing Remote Desktop Access
Remote Desktop Access provides connectivity to a server without being physically present. One way to do this is through SSH logins. It requires a private key for authentication and provide an encrypted connection.
14. Limiting Server Access
Limiting access from dedicated to cloud servers is an element of basic and advanced security measures. Restrict access based on user roles, ensuring everyone has the necessary access – nothing more.
Leading companies proactively limit server access by implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). It grants only required permissions to specific roles. Companies also use advanced measures like Privileged Access Management (PAM) systems.
They also adopt the principle of Least Privilege (PoLP), granting users the minimal levels of access necessary. AI-based threat detection is increasingly adopted to identify abnormal behaviour and potential security risks.
15 Two-Factor Authentication

Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is an essential measure for robust server security. It adds another verification layer of security to the login process. Besides a password, it requires a second factor, often a one-time code or a biometric input. The dual-check system mitigates the risk of password breaches, providing real-time alerts for attempted security intrusions.
16. Regularly Testing Security Measures
It is important to regularly test your security measures, including security software, for any flaws or weaknesses. Regular security testing should be part of your server security checklist. It helps you identify server vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, making your web server secure.
17. File Auditing and Service Auditing
File auditing is an effective strategy for pinpointing unwanted system modifications. This practice preserves your system’s “healthy state” record, against which current states can be compared. Any inconsistencies can be tracked to their origin, reinforcing server security.
Service auditing captures your services, protocols, and communicating ports. This knowledge aids in tailoring robust protection against potential intrusion points in the system and establishing a proactive server security checklist.
18. Creating Virtual Environment Isolation
Creating isolated virtual environments is a great alternative if dedicated server hardware isn’t feasible. These isolations can help mitigate security issues while safeguarding other components of data.
Options for these virtual environments include easy-to-set-up containers VM virtualisation or creating chroot jails for a UNIX operating system. The method separates a process from the system’s root directory and restricts access.
19. Disaster Recovery Plan

Despite adopting the best security practices, having a recovery plan in case of a server compromise is crucial. The plan should cover the processes and tools used to protect and recover data running on your server. Maintaining server security protects valuable data and assets, mitigating security problems and the risk of data loss. Securing your server is paramount, and adhering to these practices is a significant step.
20. Intrusion Detection Systems
Heighten server security with an Intrusion Detection System (IDS), which observes your server’s operations for unusual activities. IDS can be automated for routine scans, manually run, or programmed to monitor day-to-day operations for increased server security.
FAQs
1. What is server security?
Server security is a step to shield valuable data on your server from threats such as brute force attacks and attackers aiming to gain access.
2. Why do I need to secure my web server?
You must secure your web server because it holds important data and breaches will lead to heavy losses. Security measures keep the system safe from any attacker who wants to get in. The need to secure your server using various cyber security measures is essential for the overall integrity of your data and brand reputation.
3. How can I increase the security of my servers?
For the safety of your servers, limit access, stop services you don’t need, set up a VPN, and use SSH Secure Shell to establish a secure connection.
4. Can Linux systems help with securing servers?
Yes. The Linux operating system offers tools for jacking up server security and lowering risks by hardening the system against weak points.
5. What are some common server security issues?
Common attacks include trying many passwords until one works (brute force), looking for weak spots (vulnerability audits), or using fake IP addresses to trick into getting access.
6. How does physical security relate to server protection?
Physical safety means defending against real-world harm like theft or damage besides cyber threats, which helps maintain overall severe health.



